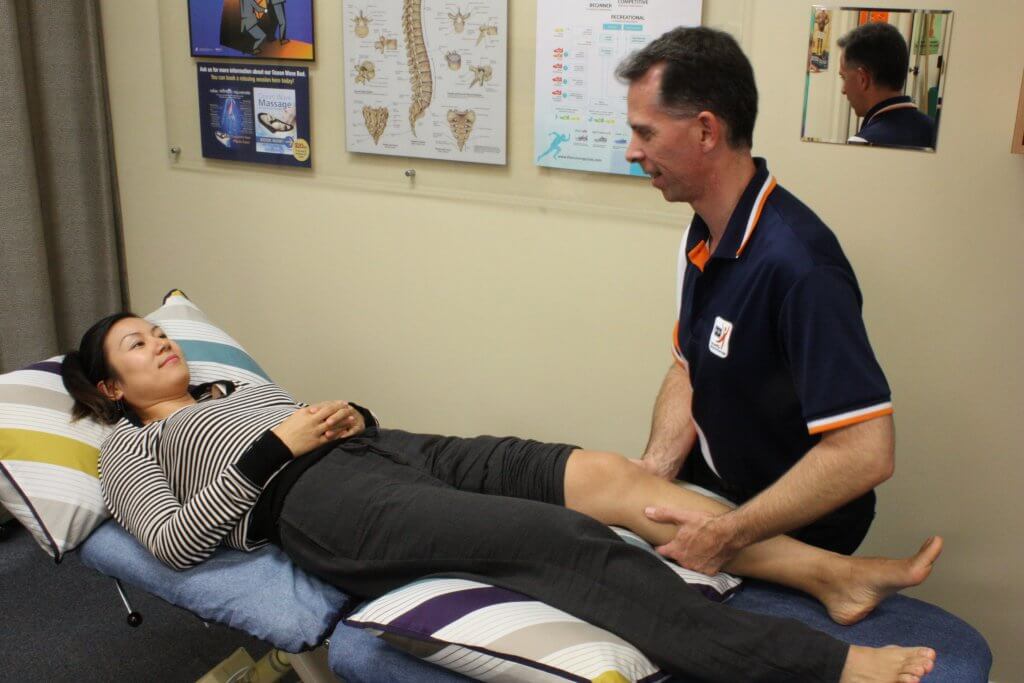
Physiotherapy treatment aims to correct postures and movements which lead to injury or damage to the body.
If you have suffered an injury such as a ligament sprain or muscle strain, the physio treatment augments the body’s normal healing process and will speed the recovery of a strong tissue repair. Regaining muscle control and strength is always a focus of treatment because it will reduce the recurrence of symptoms.
Physiotherapy treatment involves a combination of:
- joint mobilisations to loosen stiff joints
- massage releases to reduce muscle knots and spasm
- exercises and stretches to improve control, balance, strength and flexibility
- dry needling to release muscle trigger points, reduce pain and improve healing of tendinopathy
- strapping to support damaged joints, ligaments or muscles and improve posture
- posture, lifestyle and ergonomic advice to identify causative factors for your problem
- electrotherapy machines to improve healing rates and reduce pain
Each session will usually comprise of 30 minutes of hands-on or in-contact treatment plus another 15-30 minutes of exercises, dry needling or electrotherapy machine treatment. Your physiotherapist will explain to you the reason for your pain, the plan for treatment and, when possible, outline your recovery timeframe. How often we recommend you attend treatment depends on the nature of your condition, along with practical considerations such as your time and financial constraints.
The treatment may be anywhere from painless to moderately painful if it is required to gain improvement. It may be ok for you to take analgesic medication prior to attending treatment, just ask the physio. Some post-treatment discomfort or soreness is common, hopefully only for a day or so. If your physio is concerned about your injury he/she will refer you for investigations or to an appropriate medical professional for review. Likewise, if your physio believes that another form of treatment will be of benefit he/she will suggest it and refer you to an appropriate professional.